本文的分析基于Android 8.1源码。
本文章将分三篇为大家讲解。
第二篇:Android Framework之Activity启动流程(二)
第三篇:Android Framework之Activity启动流程(三)
在文章的起始,插张时序图,先看结论再看过程。(右键-新标签页打开)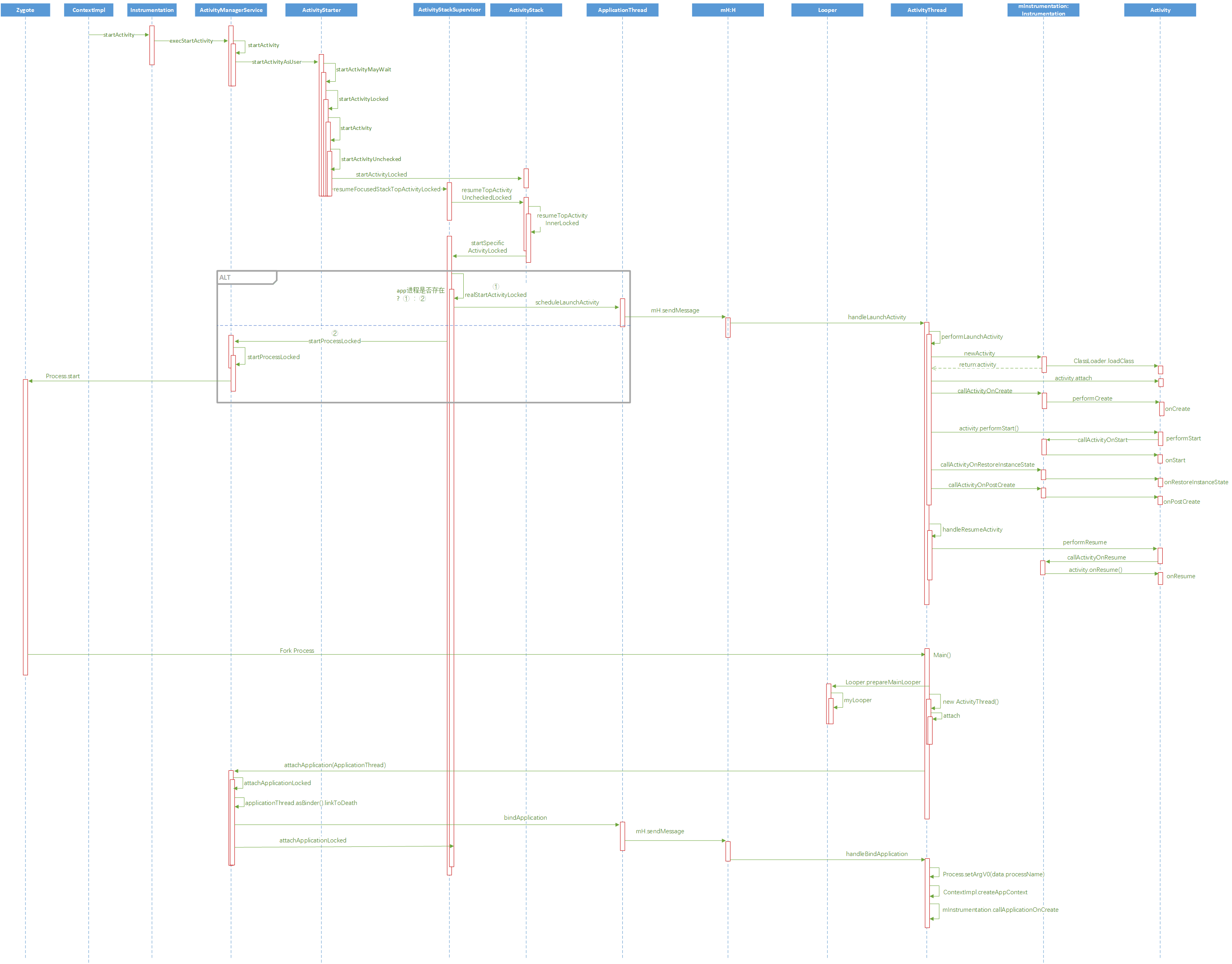
Zygote
在Android系统中,是由ActivityManagerService负责为应用程序创建新进程的。至于ActivityManagerService本身进程,则是由Zygote负责启动。
Zygote翻译成中文,是受精卵。至于为啥叫这个名字,问设计Android系统的攻城狮去……
哈哈哈,开个玩笑。。。
在Android中,大部分的应用进程都是由zygote来创建的,是不是跟受精卵的职责有点类似, emmm……
我们来看看Zygote是如何创建ActivityManagerService进程的。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
1 | public static void main(String argv[]) { |
接下来就不进去看了,贴个Zygote.forkSystemServer方法的注释吧
1 | /** |
SystemServer进程启动时,会顺带初始化ActivityManagerService,代码这里就不贴了,大家自己去搜就行。
路径:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
搜索关键字: ActivityManagerService
Context.startActivity()
当我们需要打开一个Activity时,是不是经常这样干。
这里的Context并不是Context类,真正干活的是ContextImpl。
我们来看看具体的代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public void startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle options) {
// ……我是省略号
mMainThread.getInstrumentation().execStartActivity(
getOuterContext(), mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), null,
(Activity) null, intent, -1, options);
}
Instrumentation
ContextImpl又雇佣了Instrumentation来帮它干活。
来看看具体的细节:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java
看看官方对Instrumentation的解释:
https://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Instrumentation.html
没有梯子的小伙伴们 请点我
简单来说,Instrumentation最主要的作用就是监控系统和应用的交互1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
//……省略代码
try {
//……省略代码
//关键,通过Binder实现进程间通信
//api26以前,这里应该通过ActivityManagerNative中的ActivityManagerProxy来获得AMS的代理对象
//ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startActivity();
//在api26以上,ActivityManagerProxy以及被弃用,取而代之的是以下这句
int result = ActivityManager.getService()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}
我们看看ActivityManager.getService()方法
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManager.java1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
protected IActivityManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
};
getService()中调用了IActivityManagerSingleton.get()方法,而IAtivityManagerSingleton是一个单例类。
这里可以看出IActivityManagerSingleton中采取了AIDL的方式与AMS实现了进程间通信。
因此execStartActivity()方法中的代码逻辑实际上走到了AMS的startActivity()
ActivityManagerService
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
ActivityManagerService#startActivity()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {
//判断调用者进程是否被隔离,若是,则会抛出SecurityException异常
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
//判断调用者是否有权限
userId = mUserController.handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(),userId, false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage,intent,resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, "startActivityAsUser");
}
在startActivity()中return了startActivityAsUser()方法,其中多了一个参数,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId(),这个参数会获取调用者的UserId,AMS根据UserId确定调用者的权限。最后逻辑转移到了ActivityStarter类。
//========================分割线 ==========================//
接下来的逻辑可能会引起各位看官的强烈不适,但不管怎样还是要坚持看完。
以下内容涉及到ActivityStarter.java, ActivityStackSupervisor.java,ActivityStack.java以及ActivityThread.java,接下来慢慢分析这几个类的作用。
ActivityStarter
ActivityStarter是加载Activity的控制类,收集所有的逻辑来决定如何将Intent和Flags转为Activity并将其与Task和Stack关联。
ActivityStarter# startActivityMayWait()
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStarter.java
ActivityStarter的调用流程:
- startActivityMayWait()
- startActivityLocked()
- startActivity()
- startActivityUnchecked()
1 | final int startActivityMayWait(……){ |
在ActivityStarter#startActivityLocked()里会调用ActivityStarter#startActivity(),在这里创建了ActivityRecord对象,存储Activity的重要信息。
ActivityStarter#startActivity()
这个方法是不能被外界调用的,必须通过startActivityLocked来调用。
1 | private int startActivity(/*省略参数*/){ |
在startActivity()重载方法里会执行
ActivityStarter# startActivityUnchecked()
该方法中会涉及到Android的启动模式和位运算,如果对位运算不熟悉的可以 点我 来加深印象。
1 | private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord, |
总结来讲startActivityUnchecked主要是处理栈配置和管理相关的逻辑。
ActivityStackSupervisor、ActivityStack
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
见ActivityStarter# startActivityUnchecked() 的注释1,新开启的Activity会调用
ActivityStackSupervisor #resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked().
接下来是ActivityStackSupervisor.java,相信你看到这里已经眼花缭乱了,其实我也一样,为了研究Activity的启动流程,不得不坚持 read the fucking source code.
什么?讲脏话?NO,NO,不存在的。
简单说一下ActivityStack和ActivityStackSupervisor这两个类吧。
ActivityStack:负责管理在Stack和Task中的Activity
ActivityStackSupervisor:负责管理Stack和Task的操作,可以理解为管理ActivityStack
两者相互调用, 最终完成启动Activity。
看看这两个类中的代码是如何调用的。是不是有点想骂*(手动屏蔽)的冲动。
ActivityStackSupervisor#resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked() ->
ActivityStack#resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked()->
ActivityStack#resumeTopActivityInnerLocked()->
ActivityStackSupervisor# startSpecificActivityLocked ()->
ActivityStackSupervisor # realStartActivityLocked ()
重点看看ActivityStack#resumeTopActivityInnerLocked()
在使用Android Studio进行代码跟踪,发现走的是以下流程。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options){
final ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(true /* focusableOnly */);
final boolean hasRunningActivity = next != null;
mStackSupervisor.cancelInitializingActivities();
……
//重点看这里,这里调用了StackSupervisor# pauseBackStacks方法,
//该方法会遍历所有任务栈,并调用ActivityStack#startPausingLocked()
//暂停处于栈内的所有Activity
boolean pausing = mStackSupervisor.pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, next, false);
if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
……
} else {
//调用了ActivityStackSupervisor# startSpecificActivityLocked
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
}
}
ActivityStackSupervisor# startSpecificActivityLocked()
1 | void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, |
这里有两种情况,
① 注释2处:创建activity之前进程存在,则会执行realStartActivityLocked()
② 注释3处:创建activity之前进程不存在,ActivityManagerService会调用startProcessLocked()方法创建一个新进程。
先来看第一种情况:
ActivityStackSupervisor#realStartActivityLocked()
见名知意,这里应该就是真正启动Activity的地方。难道到这里就结束了吗?并不是的,具体还请各位看官继续往下翻。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
//获得已存在的Task和Stack
final TaskRecord task = r.getTask();
final ActivityStack stack = task.getStack();
//推迟resume,避免在一个循环中多次resume
beginDeferResume();
//开始冻结屏幕
r.startFreezingScreenLocked(app, 0);
//开始收集启动信息
r.startLaunchTickingLocked();
r.app = app;
if (checkConfig) {
final int displayId = r.getDisplayId();
final Configuration config =mWindowManager.updateOrientationFromAppTokens(
getDisplayOverrideConfiguration(displayId),r.mayFreezeScreenLocked(app) ? r.appToken : null, displayId);
//当显示方向改变时,推迟resume,防止启动多余的Activity
mService.updateDisplayOverrideConfigurationLocked(config, r, true /* deferResume */,displayId);
}
//更新进程使用情况
mService.updateLruProcessLocked(app, true, null);
//更新进程OomAdj
mService.updateOomAdjLocked();
try {
//如果ProcessRecord为空,则抛异常
if (app.thread == null) {
throw new RemoteException();
}
……
//更新package最后一次使用的时间
mService.notifyPackageUse(r.intent.getComponent().getPackageName(),
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_ACTIVITY);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(mService.mTopProcessState);
//官方解释:可能用户是从系统进程启动的Activity,如果那样的话就不会走到//用来创建新配置的Binder接口,因此先在这里创建一个配置
final MergedConfiguration mergedConfiguration = new MergedConfiguration(
mService.getGlobalConfiguration(), r.getMergedOverrideConfiguration());
r.setLastReportedConfiguration(mergedConfiguration);
//通过Binder调用ApplicationThread的scheduleLaunchActivity()
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken, System.identityHashCode(r),r.info,mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,
r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,
r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
// …… 处理进程臃肿的情况
} catch(RemoteException e){
……
//会进行两次操作,第一次重启进程失败后再抛出异常执行第二次操作
//第二次失败后就放弃
}
}
realStartActivityLocked方法主要干了两件事:
① 更新AMS中各种配置
② 调用ApplicationThread# scheduleLaunchActivity()启动Activity
ActivityStackSupervisor#realStartActivityLocked()结束
ApplicationThread# scheduleLaunchActivity()的情况以及第二种进程未启动的情况将在第三篇文章为各位看官分析进程的创建和启动,敬请期待。
想直接看第三篇的朋友 请点我
下一篇:Android Framework之Activity启动流程(二)
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/chenkai19920410/article/details/54344295
https://blog.csdn.net/gaugamela/article/details/53183216
https://blog.csdn.net/Gaugamela/article/details/53895040

